For those who take a look at the lightning card close to the port of Singapore, you are going to understand a extraordinary sequence of intense lightning job without delay above essentially the most loaded re -founding strip on the planet. It seems that lightning in point of fact reacts to ships, or, quite, the tiny debris that they emit.
The usage of knowledge from the worldwide zipper detection community, my colleagues and I studied, as exhaust feathers from ships are related to an build up within the lightning frequency.
For many years, the emissions of ships have grown often, since an build up in international business resulted in a better motion of ships. Then, in 2020, new world laws decreased SHIPS sulfur emissions by means of 77 %.
Our just lately revealed learn about displays how zipper, in comparison to transport stripes, fell nearly part all through the evening after the access into drive of the principles.
The supply of the strip (higher symbol) and lightning blows (under) close to the port of Singapore. (Chris Wright)
This unplanned experiment demonstrates how thunderstorms that may be 10 miles in peak are delicate to the radiation of debris, which might be not up to sand grain.
The responsiveness of lightning to human air pollution is helping us to change into nearer to working out the lengthy -standing secrets and techniques: to what extent, if any, human emissions impact thunderstorms?
Aerosol debris can impact the clouds?
Aerosol debris, sometimes called debris, are in every single place. A few of them upward thrust by means of the wind or are comprised of organic resources, similar to tropical and boreal forests. Others are generated by means of human commercial job, similar to shipping, agricultural combustion and manufacturing.
It’s tricky to believe, however in a single liter of air – the scale of a bottle of water – there are tens of hundreds of tiny suspended liquid clusters or solids. In a polluted town, there is also hundreds of thousands of debris in step with liter, most commonly invisible to the bare eye.
Those debris are a key aspect within the formation of clouds. They function seeds or nuclei for a water vapor to condense into droplets. The extra aerosol debris, the extra cloud drops.
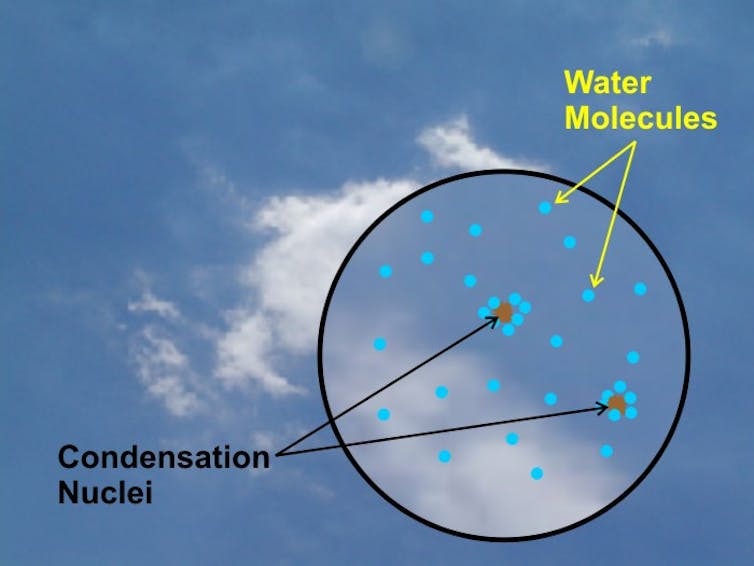 Water molecules condenses across the nuclei, forming clouds. (David Babb/Penn State, CC by-NC)
Water molecules condenses across the nuclei, forming clouds. (David Babb/Penn State, CC by-NC)
In small clouds, similar to overweight curly clouds that you’ll be able to see on a sunny day, the presence of extra seeds has an impact, making the cloud brighter, as a result of expanding the outside space of the drop will scatter extra mild.
On the other hand, in hurricane clouds, those further drops freeze in ice crystals, which makes the affect of aerosol debris on storms to mend. Freezing cloud drops releases hidden warmth and ends up in the cut up of the ice.
That is freezing together with robust thermodynamic instability, which generate storms, creates a device this is very chaotic, which makes it tricky to isolate how they’re suffering from which one issue.
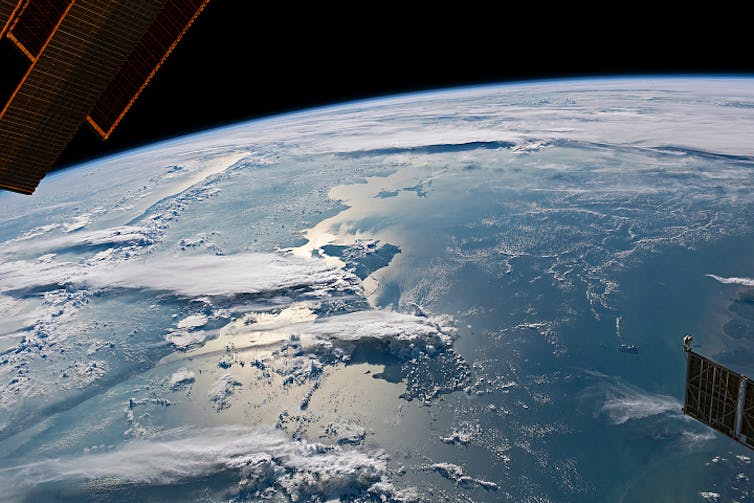 The view from the World Area Station displays the anvils of tropical thunderstorms when the nice and cozy ocean air collides with the mountains of Sumatra. (NASA Visual Earth)
The view from the World Area Station displays the anvils of tropical thunderstorms when the nice and cozy ocean air collides with the mountains of Sumatra. (NASA Visual Earth)
We can not generate a thunderstorm within the laboratory. Nonetheless, we will learn about a random experiment performed in essentially the most loaded hall on the planet.
Send and Lightning emissions
With engines, which incessantly have 3 flooring prime and burn a viscous gasoline oil, ships touring to the ports and from them, distinguish ample quantities of soot and sulfur debris.
Transportation by means of transport close to the Singapore port – essentially the most energetic business on the planet – about 20 % of the worldwide bunning oil utilized by ships are received there.
To restrict toxicity to folks close to ports, the World Marine Group – the United Countries Company, which observes the principles of supply and safety – started to keep an eye on sulfur emissions in 2020.
Within the port of Singapore, gasoline gross sales with a prime content material of sulfs fell sharply from nearly one hundred pc of the send gasoline to legislation to twenty-five % after changing gasoline with a low sulfa content material.
However what’s the angle to lightning, the emissions are associated with lightning?
Scientists have proposed numerous hypotheses to give an explanation for the correlation between lightning and air pollution, which rotate across the day of the cloud: a conflict between snowflakes of ice crystals and extra dense items of ice.
When charged, mild ice crystals are raised when a denser ice falls, the cloud turns into an enormous capacitor, expanding electrical power when ice crystals ruin thru every different. In any case, this capacitor is discharged and shoots a lightning bolt, 5 occasions scorching than the outside of the solar.
We predict that one way or the other, aerosol debris from the smoke pipes of ships generate extra ice crystals or extra widespread clashes within the clouds.
In our final learn about, my colleagues and I describe how the zipper for transportation of transportation fell by means of about 50 % after 2020. There have been no different elements, such because the affect of El -Nigno or adjustments within the frequency of thunderstorms that might provide an explanation for the unexpected lower within the job of lightning. We got here to the belief that lightning -fast job fell from the legislation.
A lower in sulfur within the gasoline of the send intended much less seeds for condensation of water drops and, in consequence, much less charging clashes between ice crystals. In the end, there have been fewer storms that have been somewhat electrified for the manufacturing of lightning immediate stroke.
What subsequent?
Much less lightning does now not essentially imply much less rain or much less storms.
There may be nonetheless a lot to learn the way folks modified the storms and the way we will exchange them at some point, deliberately or now not.
Do aerosol debris in point of fact revive the storms generally, making a extra in depth, violent vertical motion? Or the results of aerosols explicit to idiosyncrazia of lightning technology? Did folks exchange the lightning frequency world wide?
My colleagues and I paintings to reply to those questions. We are hoping that, working out the affect of aerosol debris on lightning, thunderstorms and cloud building, we will higher are expecting how the local weather of the Earth will react, since human emissions proceed to differ.![]()
Chris Wright, researcher in atmospheric science, local weather exchange program, College of Washington
This text used to be reprinted from a dialog on Inventive Commons. Learn the unique article.



